Mole, Warts & Cyst Removal – Safe and Scar-Free Procedures
Quick and effective treatments to remove unwanted moles, warts, and cysts. Restore clear, healthy skin with safe procedures and minimal downtime.
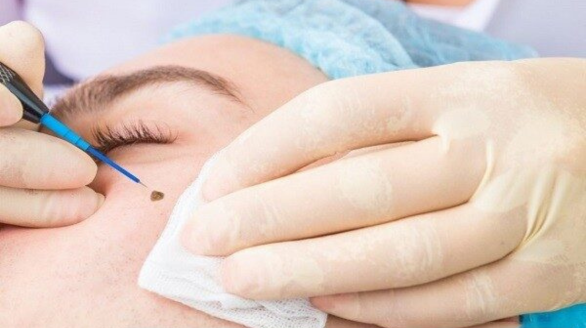
Mole, Wart, and Cyst Removal
Mole, wart, and cyst removal procedures are designed to safely eliminate unwanted or bothersome skin growths. These lesions may be removed for cosmetic reasons, to relieve irritation or discomfort, or when there’s a medical concern such as potential malignancy.
What Are Moles, Warts, and Cysts?
Moles:
Moles are clusters of pigmented skin cells (melanocytes) that appear as small brown, black, or flesh-colored spots. While most moles are benign, any mole that changes in size, color, or shape should be evaluated to rule out skin cancer.
Warts:
Warts are rough, raised bumps caused by the human papillomavirus (HPV). They can appear anywhere on the body but are most common on the hands, feet, and face. Warts can spread through direct contact and may recur without proper treatment.
Cysts:
Cysts are noncancerous sacs filled with fluid, pus, or other material. They often develop due to clogged glands, infections, or foreign substances. Although cysts are usually harmless, they can become painful or infected and may need to be removed.
Who Is a Good Candidate for Mole, Wart, or Cyst Removal?
You may be a good candidate for removal if you have:
A mole that has changed in color, size, or shape.
Warts that are painful, spreading, or resistant to over-the-counter treatments.
A cyst that is infected, swollen, or causing discomfort.
Lesions that are cosmetically undesirable or cause irritation from clothing or shaving.
A doctor’s recommendation to remove a suspicious growth for biopsy or cancer prevention.
Most people with stable health and realistic expectations are suitable for these minor procedures.
Book Your Consultation in Jaipur Today!
Types of Mole, Wart, and Cyst Removal Treatments
1. Excision (Surgical Removal):
The growth is cut out with a scalpel after numbing the area with local anesthesia. The wound may be closed with sutures and heals within one to two weeks. This method is commonly used for larger moles or cysts.
2. Cryotherapy (Freezing):
Liquid nitrogen is applied to freeze and destroy the tissue. The lesion gradually scabs and falls off in about 7–10 days. Cryotherapy is most effective for treating warts and small, benign growths.
3. Laser Removal:
A high-intensity laser beam precisely targets the growth, minimizing damage to surrounding skin. Laser removal is ideal for cosmetic mole removal or flat warts, leaving minimal scarring and fast recovery.
4. Electrosurgery or Cauterization:
An electrical current burns and removes the growth while sealing blood vessels. This method is often combined with curettage (scraping) for wart or cyst removal.
5. Drainage or Enucleation (for cysts):
If a cyst is infected, it may first be drained. Complete surgical removal (enucleation) of the cyst sac is required to prevent recurrence.
What to Expect During and After the Procedure
During the Procedure:
The area is cleaned and numbed using local anesthesia.
The chosen removal method is performed (cutting, freezing, or laser).
The entire process usually takes 15–30 minutes depending on the size and number of lesions.
If necessary, the tissue is sent to a lab for biopsy and analysis.
After the Procedure:
The treated area is bandaged, and mild redness or swelling is normal.
You may be instructed to apply antibiotic ointment and keep the area clean and dry.
Healing usually occurs within 7–14 days.
Avoid direct sun exposure until the area is fully healed to reduce scarring.
Aftercare Tips
Clean the area gently with mild soap and water as advised.
Apply a prescribed antibiotic ointment or petroleum jelly.
Keep the area covered with a sterile bandage for the first few days.
Avoid scratching, rubbing, or picking at the healing site.
Use a broad-spectrum sunscreen once healed to prevent darkening of the scar.
Report any signs of infection (redness, pus, or fever) to your doctor immediately.
Results and Outlook
Most people experience smooth, blemish-free skin after healing. Scars are minimal, especially with laser or cryotherapy treatments. In cases where a mole or cyst is removed for medical reasons, results of a biopsy will guide any further care.
With proper aftercare and sun protection, the treated area blends naturally with surrounding skin over time.
Complications (Rare)
While mole, wart, and cyst removal is generally safe, some rare side effects can include:
Minor bleeding, swelling, or redness.
Infection (if not properly cleaned).
Scarring or pigment changes at the removal site.
Recurrence, especially for cysts and warts if not completely removed.
Temporary numbness or sensitivity in the treated area.
Your doctor will provide aftercare instructions to minimize these risks and ensure optimal healing.
Book Your Consultation in Jaipur Today!
Frequently Asked Questions
The procedure is generally not painful, as local anesthesia is used. You may feel slight pressure or discomfort, but pain is minimal.
Warts and cysts can occasionally return if the entire root or sac isn’t removed. Following aftercare instructions and completing treatment reduces recurrence risk.
Healing typically takes 1–2 weeks, depending on the removal method and your skin type.
Most minor removals leave little to no visible scar, especially when done by a skilled professional. Laser and cryotherapy methods result in the least scarring.
It’s not recommended. Home treatments can lead to infection, bleeding, or scarring. Always have a licensed dermatologist perform the removal safely.
If a mole changes color, grows rapidly, bleeds, or becomes irregular in shape, seek medical evaluation immediately to rule out skin cancer.
Costs vary depending on the method used and the number of lesions. Laser and surgical excisions generally cost more but provide long-term results.
Insurance may cover removal if it’s medically necessary (for example, cancer suspicion or infection). Cosmetic removals are typically not covered.
Before / After
Proven Results You Can See

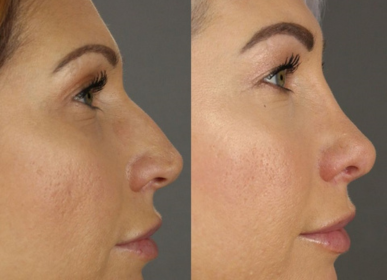

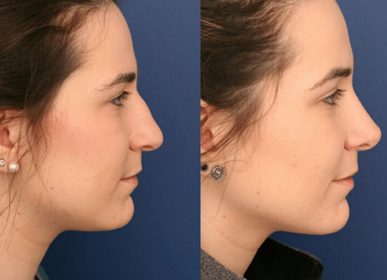
Testimonials